by Melissa Zavala in Housing News -

It’s Tax Season
I always know when tax season is just around the corner because I see Lady Liberty or Uncle Sam spinning signs that invite me into a local tax preparer’s office. Now is also a time when lots of questions arise about short sales and income taxes. If you or any of your clients participated in a short sale in 2012, then there are a number of things you will want to know about short sales and tax return preparation.
Mortgage Forgiveness Debt Relief Act of 2007
I received a 1099-MISC from the short sale lender. Is the income noted on the 1099-MISC taxable?
The Mortgage Forgiveness Debt Relief Act of 2007 provides tax forgiveness for certain short sale sellers, and such forgiveness depends on the taxpayer’s specific situation. Taxpayers who sold their home in a short sale during 2012 should seek the advice of an accountant in order to learn whether this Relief Act applies to their unique tax position.
What if the Mortgage Forgiveness Debt Relief Act doesn’t apply to my short sale?
Because the Mortgage Forgiveness Debt Relief Act of 2007 does not apply to everyone (e.g. if the home sold is not a qualified principal residence or due to bankruptcy), it is vital that taxpayers seek the advice of an accountant in order to learn about any other tax laws that may come into play in order to provide tax relief.
Is Relocation Assistance Money Taxable?
I received an incentive from the short sale lender? Do I have to pay taxes on the incentive?
According to the Internal Revenue Service, “Cash for Keys Program income, which is taxable, is income from a financial institution, offered to taxpayers to expedite the foreclosure process. Report this as ‘other income’ on Form 1040, line 21. The taxpayer should receive Form 1099-MISC with the income in box 3.”
I received an incentive from the short sale lender, but I did not receive a 1099-MISC. How should I proceed?
I’d bet dollars to doughnuts that short sale sellers often don’t receive the 1099-MISC because the short sale lender doesn’t have a record of the taxpayer’s new address. Speak with an accountant about how to proceed in this situation.
Common Problems with Relocation Assistance
My real estate agent told me that I was supposed to get relocation assistance money. We closed, and I received a 1099-MISC. However, I never got any relocation assistance money. What should I do?
All relocation assistance money is documented on the final settlement statement (also called a HUD-1) and payable to short sale sellers through the settlement agent at closing. If there is no line item for relocation assistance on the settlement statement and no notation on the short sale approval letter from the lender, then the bank did not approve the short sale assistance.
If there is a line item for relocation assistance and the seller did not receive the funds, contact the settlement agent for more information. In many cases, with prior written authorization of the short sale seller and the short sale lender, relocation assistance money is used in order to pay off non-institutional liens and clear the title for closing.
On the settlement statement, it shows that the buyer is paying the relocation assistance and not the short sale lender. Why would I receive a 1099-MISC from the short sale lender if the buyer paid the money?
Since any real estate sale requires that buyer funds be used to pay seller costs, the relocation assistance shows as a debit to the buyer and a credit to the seller. Of course, this is a credit to the seller from the short sale lender who retains all of the remaining funds at closing.
Short Sale Documentation
No matter when the short sale closes, all short sale sellers should retain copies of the short sale approval letters from the lenders and a final settlement statement from the closing agent. In this way, any questions that come up (no matter how far in the future) can be addressed quickly and efficiently.




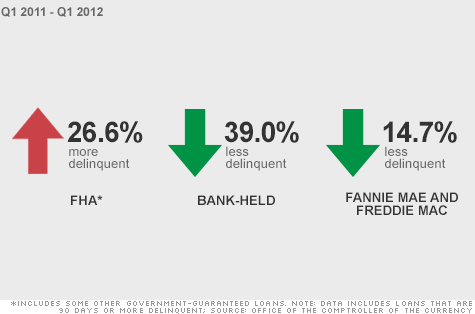 Delinquencies and foreclosures of FHA-backed mortgages are soaring, putting further strain on the housing agency’s finances and making a taxpayer bailout more likely.
Delinquencies and foreclosures of FHA-backed mortgages are soaring, putting further strain on the housing agency’s finances and making a taxpayer bailout more likely.

![[refinance]](http://si.wsj.net/public/resources/images/MI-BP578_refina_DV_20120617172748.jpg) European Pressphoto AgencyHUD Secretary Shaun Donovan says there is ‘essentially a monopoly on refinancings’ among the largest banks.
European Pressphoto AgencyHUD Secretary Shaun Donovan says there is ‘essentially a monopoly on refinancings’ among the largest banks.
![[REFINANCE]](http://si.wsj.net/public/resources/images/MI-BP567_REFINA_NS_20120617174809.jpg)

© 2013 The Peral Group